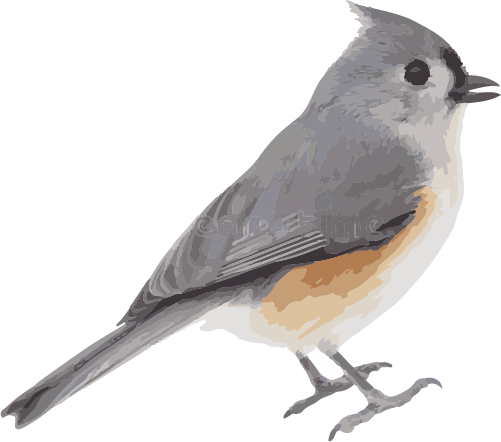








A flycatcher of wet thickets across northern North America, the Alder Flycatcher is a rather indistinct olive-green bird with bold wingbars and a distinctive, raspy song of free-beer! It’s unusual among Empidonax flycatchers for having only an indistinct pale eyering, a trait it shares with the very similar Willow Flycatcher. Alder Flycatchers thrive in open settings such as bogs and beaver ponds, where they sit on high perches and fly out to catch insects from nearby leaves or in midair.
Alder Flycatchers eat insects that they pick from foliage during short flights or catch in midair. Prey include wasps, beetles, flies, butterflies and caterpillars, and grasshoppers. Wintering birds may include fruit in their diet.
The Alder Flycatcher is a bird of wet thickets, breeding in brushy meadows, shrubby wetlands, overgrown beaver ponds, and, appropriately, in thickets of alder as well as buckthorn, willow, maple and other wetland trees. Very little is known about their wintering habitat, since it’s very difficult to differentiate Alder, Willow, and other Empidonax flycatchers without hearing their songs.
Alder Flycatchers nest low in dense, shrubby bushes.
Alder Flycatchers build an untidy and bulky cup nest of coarse grass. The nest usually has “streamers’ of moss, cattail, and grass hanging from the bottom or the rim of the nest.